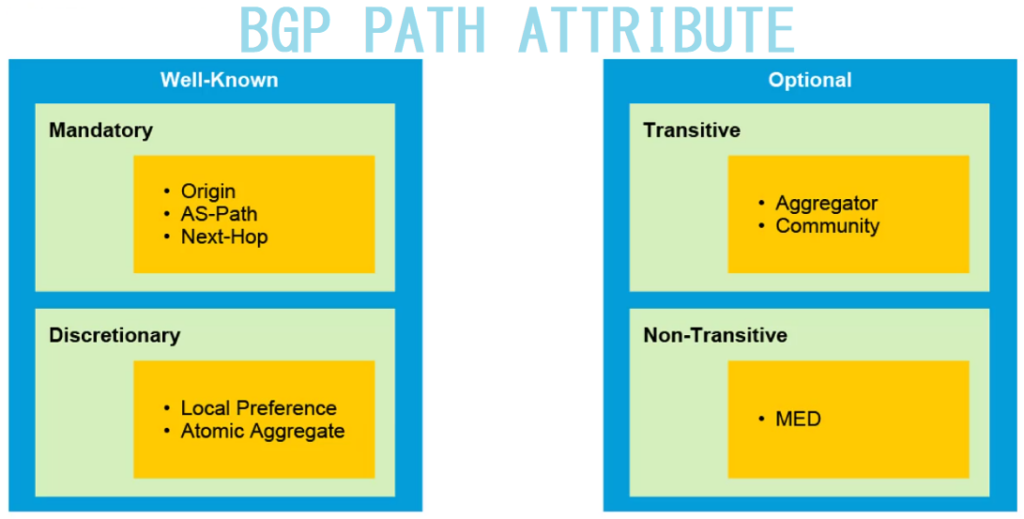
•An OSPF router ID is a 32-bit value, represented as an IPv4 address. It is used to uniquely identify an OSPF router, and all OSPF packets include the router ID of the originating router.
•Every router requires a router ID to participate in an OSPF domain. It can be defined by an administrator or automatically assigned by the router. The router ID is used by an OSPF-enabled router to do the following:
•Participate in the synchronization of OSPF databases – During the Exchange State, the router with the highest router ID will send their database descriptor (DBD) packets first.
•Participate in the election of the designated router (DR) – In a multiaccess LAN environment, the router with the highest router ID is elected the DR. The routing device with the second highest router ID is elected the backup designated router (BDR).
Router ID Order of Precedence
Cisco routers derive the router ID based on one of three criteria, in the following preferential order:
- The router ID is explicitly configured using the OSPF router-id rid router configuration mode command. This is the recommended method to assign a router ID.
- The router chooses the highest IPv4 address of any of configured loopback interfaces.
- The router chooses the highest active IPv4 address of any of its physical interfaces.
Configure a Loopback Interface as the Router ID
Instead of relying on physical interface, the router ID can be assigned to a loopback interface. Typically, the IPv4 address for this type of loopback interface should be configured using a 32-bit subnet mask (255.255.255.255). This effectively creates a host route. A 32-bit host route would not get advertised as a route to other OSPF routers.
OSPF does not need to be enabled on an interface for that interface to be chosen as the router ID.

Explicitly Configure a Router ID
In our reference topology the router ID for each router is assigned as follows:
•R1 uses router ID 1.1.1.1
•R2 uses router ID 2.2.2.2
•R3 uses router ID 3.3.3.3
Use the router-id rid router configuration mode command to manually assign a router ID. In the example, the router ID 1.1.1.1 is assigned to R1. Use the show ip protocols command to verify the router ID.

Modify a Router ID
•After a router selects a router ID, an active OSPF router does not allow the router ID to be changed until the router is reloaded or the OSPF process is reset.
•Clearing the OSPF process is the preferred method to reset the router ID.