
Default Static Route
•A default route is a static route that matches all packets. A single default route represents any network that is not in the routing table.
•Routers commonly use default routes that are either configured locally or learned from another router. The default route is used as the Gateway of Last Resort.
•Default static routes are commonly used when connecting an edge router to a service provider network, or a stub router (a router with only one upstream neighbor router).
•The figure shows a typical default static route scenario.
IPv4 Default Static Route: The command syntax for an IPv4 default static route is similar to any other IPv4 static route, except that the network address is 0.0.0.0 and the subnet mask is 0.0.0.0. The 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 in the route will match any network address.
Note: An IPv4 default static route is commonly referred to as a quad-zero route.
The basic command syntax for an IPv4 default static route is as follows:
Router(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 {ip-address | exit-intf}
IPv6 Default Static Route: The command syntax for an IPv6 default static route is similar to any other IPv6 static route, except that the ipv6-prefix/prefix-length is ::/0, which matches all routes.
The basic command syntax for an IPv6 default static route is as follows:
Router(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 {ipv6-address | exit-intf}
Configure a Default Static Route
The example shows an IPv4 default static route configured on R1. With the configuration shown in the example, any packets not matching more specific route entries are forwarded to R2 at 172.16.2.2.
R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.2
An IPv6 default static route is configured in similar fashion. With this configuration any packets not matching more specific IPv6 route entries are forwarded to R2 at 2001:db8:acad:2::2
R1(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:acad:2::2
Verify a Default Static Route
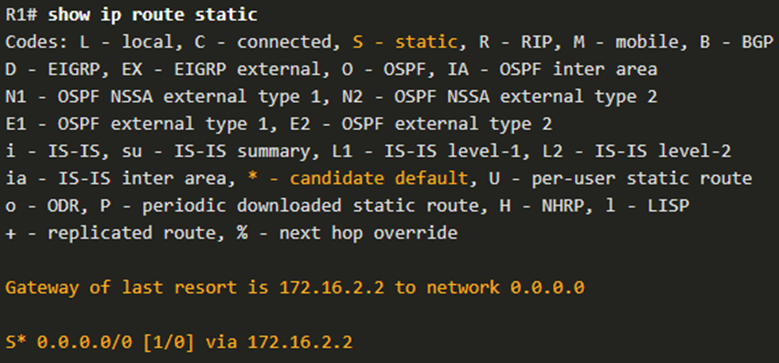
The show ip route static command output from R1 displays the contents of the static routes in the routing table. Note the asterisk (*) next to the route with code ‘S’. The asterisk indicates that this static route is a candidate default route, which is why it is selected as the Gateway of Last Resort.
Notice that the static default route configuration uses the /0 mask for IPv4 default routes. Remember that the IPv4 subnet mask in a routing table determines how many bits must match between the destination IP address of the packet and the route in the routing table. A /0 mask indicates that none of the bits are required to match. As long as a more specific match does not exist, the default static route matches all packets.
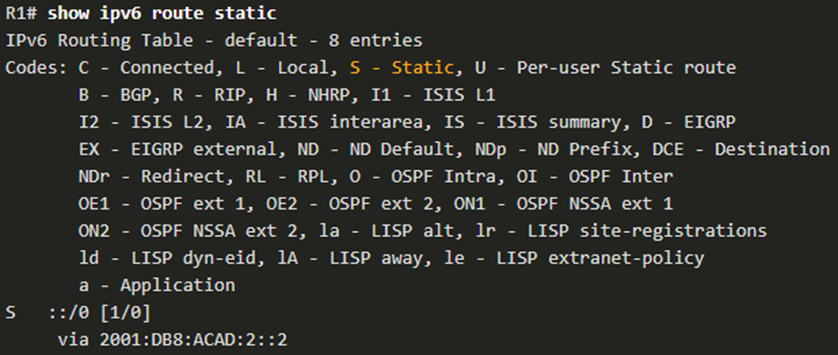
This example shows the show ipv6 route static command output to display the contents of the routing table.
Notice that the static default route configuration uses the ::/0 prefix for IPv6 default routes. Remember that the IPv6 prefix-length in a routing table determines how many bits must match between the destination IP address of the packet and the route in the routing table. A ::/0 prefix indicates that none of the bits are required to match. As long as a more specific match does not exist, the default static route matches all packets.
CCNA Classes in Dubai – CCNAGuru (Cisco Expert Trainer)
Join CCNA classes in Dubai by CCNAGuru, led by a Cisco-certified expert. Available for in-person and online classes with real lab practice, exam-focused training, and career guidance.
Introduction to Networks
Switching, Routing & Wireless
Enterprise Networking & Security
CCNA Training Across U.S. States
Explore CCNA Training Centers and Certification Courses across every U.S. state.
Connect with me: FB X IN YT TT WA
*All U.S. state pages are part of CCNAGuru.com's training network.